Contents
Preparation of carbon monoxide (CO) :
1. Carbon monoxide can be prepared by burning carbon with oxygen in limited supply of air.
![]()
2. It can also be prepared by reduction of metallic oxide with carbon ( i.e. coal or coke)

3. By passing steam over red hot coke.
![]()
Laboratory preparation of carbon monoxide(CO) gas :
Carbon monoxide gas can be prepared in lab by heating formic acid or oxalic acid with conc. H2SO4.


Procedure: Small amount of oxalic acid crystal is taken in a round- bottomed flask and all the apparatus are fitted as shown in figure. When conc. H2SO4 is poured in the flask through thistle funnel and heated then a mixture of CO and CO2 gas is formed. The mixture of gas is passed through a bottle containing NaOH solution where the CO2 gas is absorbed by NaOH.
2NaOH + CO2 → Na2CO3 + H2O
The pure CO gas is then collected in a gas jar by downward displacement of water.
Physical properties :
- It is colourless and poisonous gas (with faint smell).
- It is lighter than air.
- It is slightly soluble in water.
Chemical Properties of carbon monoxide(CO):
1. It is neutral to litmus.
2. Combustibility (Reaction with oxygen) : It is combustible but not a supporter of combustion. It burns in air to form carbon dioxide.
![]()
3. Formation of addition products :
- Action with hydrogen : When carbon monoxide gas is heated with hydrogen in presence of ZnO and Cu at 3000C then methanol is formed.

- Action with NaOH ( caustic soda): When carbon monoxide is heated with sodium hydroxide then sodium formate is formed.

{note: CO2 + NaOH → Na2CO3 + H2O}
- Action with chlorine: Carbon monoxide reacts with chlorine in presence of sunlight to produce phosgene ( carbonyl chloride) which is a poisonous gas.

- Action with sulphur : When a mixture of carbon monoxide and sulphur vapour is heated, then carbonyl sulphide is formed.
CO + S → COS (carbonyl sulphide)
- Action with ammonical cuprous chloride (solution) : When carbon monoxide gas is passed into ammonical cuprous chloride solution, an addition product i.e. cuprous carbonyl chloride is obtained.

4. Reaction with transition metals ( i.e. Formation of carbonyl compound) :
Carbon monoxide reacts with transition metals like nickel, iron, cobalt, etc. under suitable conditions to form addition compound called metal carbonyls.
Eg. When CO gas is passed into finely divided nickel at 800C, then nickel tetracarbonyl is formed.
![]()
Similarly,

{Carbonyl compound formation takes place due to presence of lone pair of electron in carbon atom of CO molecule, i.e. a Lewis base}
5. Reducing character : Carbon monoxide acts as reducing agent.
- It is used to reduce metallic oxide to metal in metallurgical process. Eg.
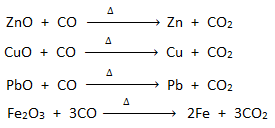
- It can reduce iodine oxide to iodine.
![]()
- Reduction of Tollen’s reagent( i.e. ammonical silver nitrate solution) : It reduces Tollen’s reagent to metallic silver.

- Reduction of Fehling’s solution : {Basic copper sulphate solution in presence of sodium potassium tartarate is called Fehling’s solution.} It reduces Fehling’s solution to red ppt. of cuprous oxide.

Uses of CO :
- It is used as reducing agent in metallurgical process.
- It is used to prepare carbonyl compounds.
- It is used to prepare poisonous gas.
Structure of carbon monoxide(CO)

Carbon monoxide toxicity :
Q) Why carbon monoxide gas is extremely poisonous( toxic) ?
→ Carbon monoxide combines with haemoglobin to form carboxy haemoglobin. This makes haemoglobin unable to carry oxygen from lungs to the different parts of the body and causes suffocation and even death. Thus CO gas is highly toxic.

{ Therefore, it is adviced that a room being heated by burning coal or other carbon rich fuel should be well ventilated.}

Some questions and answers :
Q) Carbon monoxide is used as a reducing agent in metallurgy but not carbon dioxide, why?
→ CO reduces other substance and itself oxidizes to form CO2 but CO2 already is oxidized form and can not further reduce other species. So, CO is used as reducing agent but not CO2.

Q) How would you convert CO into CO2 and vice versa ?
→ CO can be converted into CO2 by heating in the presenc of excess of air.
![]()
CO2 can be converted into CO by passing through red hot coke.
![]()
Q) Write down balanced chemical equations giving proper products for the following statements :
i. Water gas is heated over ZnO + Cu.
ii. Carbon monoxide is passed over heated caustic soda.
→ i. 
ii) 
Additional Questions from carbon :
Q) What is dry ice? Why it is called so?
→ Solid CO2 is called dry ice because its structure is similar to that of ice. When it is kept for some time then it gets evaporated without wetting the place where it is kept.
Q) How can you prove that all the allotropes of carbon contain same element?
Q) Show that diamond and graphite consist of carbon only.

![]()
→ To prove it first of all 1 gm sample of each allotropes of carbon is taken in a combustion tube and burnt with oxygen to form carbondioxide . The carbondioxide formed is passed into calculated amount of NaOH solution. In all cases the weight of NaOH solution increases. This proves all the allotropes of carbon contains same element.
References :
- Shriver, D. F., Atkins, P. W., Inorganic Chemistry, Fifth Edition, Oxford university Press, 2010.
- Agrawal, S. K., Lal, K., Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, Fifth Revised Edition, Pragati Prakashan, Meerut, 2001.
- Cotton, F. A., and Wilkinson, G., Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, Fifth edition, John Wily and Sons, Singapore, 1995.
- Day, C.M., Selbin, J., Theoritical inorganic Chemistry, second edition, Affiliated East-West Press Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 2002.
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/171876
- https://www.simply.science/images/content/chemistry/metals_and_non_metals/carbon_family/conceptmap/Carbon_Monoxide.html


![Electrochemistry – Class 11 [NEB] Chemistry](https://chemicalnote.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/aldo-keto-cover.png)
